
Let’s look at the stockholders’ equity section of a balance sheet for a corporation that has issued only common stock. There are 10,000 authorized shares, of which 2,000 shares had been issued for $50,000. At the balance sheet date, the corporation had cumulative net income after income taxes of $40,000 and had paid cumulative dividends of $12,000, resulting in retained earnings of $28,000. Company or shareholders’ equity is equal to a firm’s total assets minus its total liabilities. It can also be calculated as the sum of its share capital and retained earnings, minus its treasury shares. Stockholders’ equity can be calculated by subtracting the total liabilities of a business from total assets or as the sum of share capital and retained earnings minus treasury shares.
- Companies may have bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations under this category.
- The fundamental accounting equation states that the total assets belonging to a company must always be equal to the sum of its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
- These often involve significant long-term commitments that extend beyond the immediate operating cycle.
- Retained earnings are typically reinvested back into the business, either through the payment of debt, to purchase assets, or to fund daily operations.
- Paid-in capital is the money that a company receives when investors buy shares of its stock.
Why Does the Difference Matter to Investors?
Corporations report shareholders’ equity with line items such as common stock and retained earnings, while sole proprietorships and partnerships use owner’s or partners’ equity accounts. Shareholders’ equity is the amount that would be returned to shareholders if all the company’s assets were liquidated and all its debts repaid. Shareholders’ equity also includes retained earnings, which is the amount of profit leftover that is saved or retained and used to pay dividends, reduce debt, or buy back shares of stock. For investors, a strong and growing stockholders’ equity signals a company’s financial stability and its ability to withstand economic downturns. A consistent increase in retained earnings, a component of equity, indicates a company’s effective reinvestment of profits for long-term growth. Cash dividends decrease retained earnings, lowering the total equity balance.

Weighted-Average Number of Shares of Common Stock
- However, there have been many cases in which the assets were exhausted before shareholders got a penny.
- In other words, it represents the excess of the issue price over the nominal or par value of the shares.
- The book value of an asset is the amount of cost in its asset account less the accumulated depreciation applicable to the asset.
- Shareholders’ equity can help to compare the total amount invested in the company versus the returns generated by the company during a specific period.
- The Paid-in Capital from Treasury Stock now shows a credit balance of $170.
- The dividend on preferred stock is usually stated as a percentage of its par value.
To illustrate how preferred stock works, let’s assume a corporation has issued preferred stock with a stated annual dividend of $9 per year. The holders of these preferred shares must receive the $9 per share dividend https://ms2.inkland.com/what-is-the-percent-of-sales-method/ each year before the common stockholders can receive a penny in dividends. But the preferred shareholders will get no more than the $9 dividend, even if the corporation’s net income increases a hundredfold.
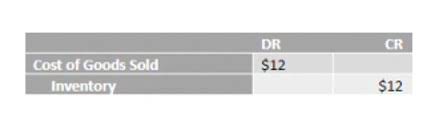
Paid-in capital
The accounting equation ensures that the balance sheet always remains in balance, reflecting how a company’s resources are funded. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (AOCI) includes gains and losses not recognized in net income on the income statement but directly affecting shareholders’ equity. These are “unrealized” gains or losses, meaning they relate to assets or liabilities not yet sold or settled. Examples Oil And Gas Accounting include unrealized gains or losses on available-for-sale securities, foreign currency translation adjustments, and certain pension plan adjustments.
How do you evaluate shareholders’ equity?
- This is especially true of companies that have been in business for many years.
- By comparing total equity to total assets belonging to a company, the shareholders equity ratio is thus a measure of the proportion of a company’s asset base financed via equity.
- When a company sells new shares (either common or preferred) to investors, it receives cash or other assets in exchange.
- Positive shareholder equity means the company has enough assets to cover its liabilities.
- But don’t worry, we’ll break it down in simple terms, so you can easily grasp these concepts and see how they affect your decisions.
For example, if total stockholders equity a company issues 1,000 shares at $10 each, its share capital equals $10,000. This financial metric is vital because it shows the net value of a company. Whether you’re running a business or investing in one, stockholders’ equity helps you evaluate its financial stability and potential for growth. Additional paid-in capital is the amount that is paid for stocks that are above their stated par value. This component of shareholders equity is computed by subtracting the par value of each common or preference share from the value they have been sold for.
The number of issued shares is often considerably less than the number of authorized shares. When its articles of incorporation are prepared, a business will often request authorization to issue a larger number of shares than what is immediately needed. The officers of a corporation are appointed by the corporation’s board of directors to carry out (or execute) the policies established by the board of directors. The officers include the president, chief executive officer (CEO), chief operating officer (COO), chief financial officer (CFO), vice presidents, treasurer, secretary, and controller.

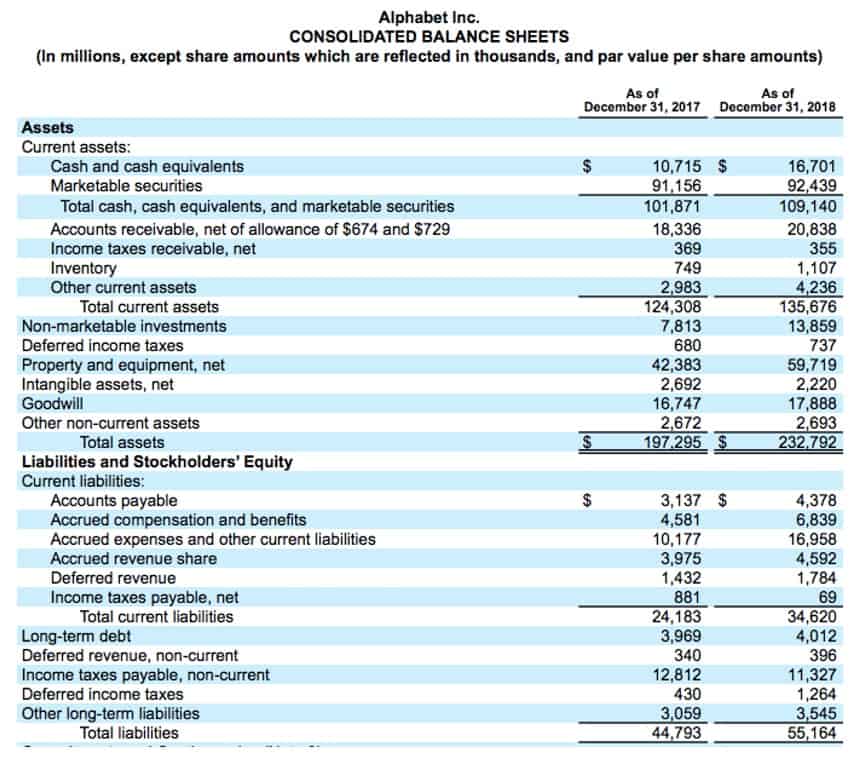
Shareholders’ equity can also be calculated by taking the company’s total assets less the total liabilities. The account demonstrates what the company did with its capital investments and profits earned during the period. The Repurchase of Stock, often referred to as a stock buyback, decreases total shareholders’ equity. When a company buys back its own shares, it removes them from circulation, reducing the treasury stock account. Shareholders’ equity signifies the portion of the company’s assets financed by its owners, either through direct investment or through retained earnings.

Negative equity signals financial distress and may indicate insolvency or the need for restructuring. Stockholders’ equity represents the owners’ residual claim after liabilities are settled, providing a snapshot of the company’s financial health. Investors analyze it to assess the company’s stability, growth potential, and ability to generate returns, aiding in informed investment decisions. While both Shareholder Equity and Net Worth refer to what is left after all debts have been paid off from total assets, they are standardly applied to different entities. Shareholder Equity is commonly used in the context of corporations, highlighting the net asset ownership spread among investors. Net Worth, on the other hand, is often used in the context of individuals or non-corporate entities representing their total wealth.
